Evolutionary biologists sequenced seahorse DNA to understand their evolution, one like no other sea creature.
It has neither a pelvic fin nor tail, males give birth, they have no teeth, and bony plates reinforce its body; the seahorse is an evolutionary oddity and it is the prime subject for six evolutionary biologists that want to understand why. Their findings were astounding; they found that the loss and duplication of genes and the loss of regulative elements directly contributed to a rapid change in evolution.
Professo Axel Meyer identified, from genomic sequencing, that several genes that are present in fish teeth as well as human teeth development, are not found in seahorses. They evolved by the way they eat food, they suck up prey rather than bite and chew.
Curiously, they found that gene duplication influenced pregnancy in males. Duplicated genes can create an entirely new function, and this just so happens to be the pregnancy in males. The genes probably only regulates the process by which the babies leave the brood, but there still is much to learn.
The seahorse is an excellent organism to study because is shows how evolution can rapidly change and organism's appearance and function.
Wednesday, December 14, 2016
The evolution of Seahorses
Labels:
Evolution,
gene duplication,
genomic sequence,
seahorse
Adapting to Pollution, Quickly.
Pollution of our waterways is becoming a problem but one particular fish has been shown to have adapted to the excess level of pollution in the waters that they live in. Atlantic killfish that occupy polluted estuaries. The Atlantic killfish is a small slender fish that is native to the North American coast. (Banded killfish facts). The places they live have toxicity levels high enough to kill them and other larger fish. This is due to industrial plants that dump their waste into the estuary. Scientists from the University of California have examined these fished in order ti figure out how they are adapting so quickly. Their tests exhibited that the killfish is 8,000 times for resistant to these pollutants than other fish. The killfish is an important small food fish, meaning that it is the base food for most other bigger fish. It also is a bio-indicator, meaning that if the killfish suddenly start to take a dive them the surrounding ecosystem will be harshly affected.
The Atlantic killfish, like the one above, is special because it has very high levels of genetic variation, higher than any other vertebrate. The more genetic variation the faster evolution can act upon that creatures. The fish were taken from a multitude of different sites, including Massachusetts, New Jersey, Connecticut, and Virginia. Their test also concluded that their high levels of genetic variation were not due to the polluted enviorment, instead they were already present in the fish's genome. The Atlantic killfish has had the ability to adapt very quickly to changing enviorments. The study lay the frame for future research that can figure out which genes are used to deal with the chemical change. (University of California- Davis).
Banded killifish photos and facts. (n.d.). Retrieved December 14, 2016, from http://www.arkive.org/banded-killifish/fundulus-diaphanus/
University of California - Davis. (2016, December 8). Against the tide: A fish adapts quickly to lethal levels of pollution: What's its secret? And can humans learn from it?. ScienceDaily. Retrieved December 14, 2016 from www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2016/12/161208143334.htm
Labels:
Adaptation,
Evolution,
Genetic Variation,
Killfish,
pollution
Salt Tooth
Most people have heard of a sweet tooth but in recent discovery, there is also a gene relating to a "salt tooth"! During a study, the people with a variation of the gene, TAS2R48, were more likely to eat too much sodium or acquire a "salt tooth". There is a correlation between people with high blood pressure and their salt-intake. The study was presented as the American Heart Association's Scientific Sessions and many people found that identifying a gene like this is very helpful. If people know that they have the particular variation in the gene then they can be given individual guidance to help them prevent diseases like heart disease. People with the variation in the gene should eat about half the recommended amount of sodium (half of 2,300 mg).
When a gene like this is found it doesn't seem like it would be useful but then it was applied to a disease like heart disease it is very useful. I am curious to see the extent of the study and how far the identification of the gene helps other people. Maybe the discovery can lead to more identifications of genes!
Source: (other source in text)
http://www.livescience.com/56850-salt-taste-genetics.html
Labels:
#gene #variation,
#genetics,
#heartdisease,
#salt
Temperature Dependent Bacteria as a Remedy
A new study conducted at the Massachusetts Institute
of Technology shows that temperature dependent bacteria may be used in the
future. This treatment will be administered to patients by placing bacteria in
them. The bacteria will contain medicine that will be pumped into the body
based on the temperature of the bacteria. The bacteria will be changed in
temperature by use of ultrasound technology. Furthermore, if the individual has
a fever this will cause the bacteria to self-destruct and be expelled from the
body through defecation. This treatment may be useful in cancer patients
because bacteria tend to gravitate toward tumors. This is due to tumors
containing less oxygen.
This is
very interesting and informative. I hope to see more information on this topic in
the future. This will be very useful in medicinal technology. Doctors should look
more into this technology to treat their patients.
Labels:
Bacteria,
Biological Studies,
cancer,
cancer treatments,
Mice Studies,
MIT
Why Left Handedness?
Why is left handedness so puzzling? It only accounts for 12% of the world's population. Yet, so many famous people have been left handed as well as five out of our last seven presidents to Einstein to the first man on the moon. What is it, genetically speaking, about left handedness, that explains this phenomenon?
To begin, the left handed origins have been observed in Neanderthals. Scientists studied the grooves in their teeth from them scratches they made while carving their food up and found that one in every ten Neanderthal scratched their teeth towards the left side. This can give us some insight as to how long the genes have influenced left handedness. However, scientists still do not understand what genes and how many are in play to cause left handedness.
We do have a clue as to how it affects left handed people, however. Left handedness and intelligence seem to go hand in hand. Left handers disproportionately make up the small amount of people with a genius iq. For example, twenty percent of Mensa members (society where one must have a high iq) are left handed. For only about ten percent of left handed people making up the population, this is an interesting fact. There are some drawbacks to being left handed, however. 40% of schizophrenic people are left handed. Scientists believe this happens to left handed people who have equal access to both sides of the brain. This can cause complex messages to the brain that can result in misconnections in neural networks and thus causing the symptoms of schizophrenia. The science is not in on this yet, however.
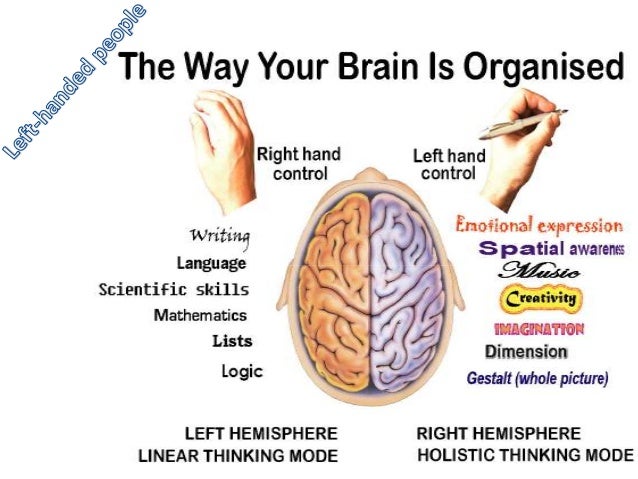
One thing is for sure. Left handedness should be studied more and understood. Many household names are left handed people that changed the world with their way of thinking. Science could have a breakthrough if they can understand how schizophrenia develops by studying the biological markers in left handed people. In any case, the left handed people are an important anomaly to understand, and essential in shaping our music, politics, and technology.
http://www.mirror.co.uk/news/technology-science/science/lefty-righty-here-astonishing-statistics-4757193
http://www.bbc.com/future/story/20160930-the-mystery-of-why-left-handers-are-so-much-rarer
http://www.anythinglefthanded.co.uk/being-lh/lh-info/advantages.html
http://healthland.time.com/2013/11/01/the-connection-between-left-handedness-and-schizophrenia/
To begin, the left handed origins have been observed in Neanderthals. Scientists studied the grooves in their teeth from them scratches they made while carving their food up and found that one in every ten Neanderthal scratched their teeth towards the left side. This can give us some insight as to how long the genes have influenced left handedness. However, scientists still do not understand what genes and how many are in play to cause left handedness.
We do have a clue as to how it affects left handed people, however. Left handedness and intelligence seem to go hand in hand. Left handers disproportionately make up the small amount of people with a genius iq. For example, twenty percent of Mensa members (society where one must have a high iq) are left handed. For only about ten percent of left handed people making up the population, this is an interesting fact. There are some drawbacks to being left handed, however. 40% of schizophrenic people are left handed. Scientists believe this happens to left handed people who have equal access to both sides of the brain. This can cause complex messages to the brain that can result in misconnections in neural networks and thus causing the symptoms of schizophrenia. The science is not in on this yet, however.

One thing is for sure. Left handedness should be studied more and understood. Many household names are left handed people that changed the world with their way of thinking. Science could have a breakthrough if they can understand how schizophrenia develops by studying the biological markers in left handed people. In any case, the left handed people are an important anomaly to understand, and essential in shaping our music, politics, and technology.
http://www.mirror.co.uk/news/technology-science/science/lefty-righty-here-astonishing-statistics-4757193
http://www.bbc.com/future/story/20160930-the-mystery-of-why-left-handers-are-so-much-rarer
http://www.anythinglefthanded.co.uk/being-lh/lh-info/advantages.html
http://healthland.time.com/2013/11/01/the-connection-between-left-handedness-and-schizophrenia/
Tibetan Dogs Able to Survive High Altitudes
A recent study shows that Tibetan dogs may have inherited their fitness at high-altitude, from breeding with Tibetan gray wolves around 24,000 years ago. This discovery somewhat mirrors the way that humans living at this altitude also inherited this type of fitness. Tibetans were found to have inherited this type of "high altitude gene" from and ancient, now extinct, species of human known as Denisovans, that another study found that humans interbred with around 40,000 years ago. This "high altitude gene" is a variant of a gene called EPAS1 that is found in the Tibetan mastiffs and regulates the production of hemoglobin. Scientists found that the most likely source of this variant of the gene in the Tibetan dogs, most likely came from the gray wolf.
Gray wolves also have a variant of the EPAS1 gene and found that the Tibetan gray wolf and Tibetan dogs most likely interbed 24,000 years ago, possibly from Tibetan dogs traveling with humans to higher altitudes. Another recent study showed that dogs may have only been domesticated around 16,000 years ago so this may show that the Tibetan mastiff may be one of the first and oldest dog breeds. The way this sort of mirrors how humans have been able to adapt to higher altitudes really shows how much different species have in common when it comes to the process of evolution, and makes you wonder why certain species interbred and what each species may have gotten out of it.
://www.sciencemag.org/news/2016/12/tibetan-dogs-can-survive-high-altitudes-thanks-ancient-breeding-wolves
http://www.theanimalfiles.com/mammals/carnivores/wolf_grey.html
http://science.sciencemag.org/content/333/6046/1084
Gray wolves also have a variant of the EPAS1 gene and found that the Tibetan gray wolf and Tibetan dogs most likely interbed 24,000 years ago, possibly from Tibetan dogs traveling with humans to higher altitudes. Another recent study showed that dogs may have only been domesticated around 16,000 years ago so this may show that the Tibetan mastiff may be one of the first and oldest dog breeds. The way this sort of mirrors how humans have been able to adapt to higher altitudes really shows how much different species have in common when it comes to the process of evolution, and makes you wonder why certain species interbred and what each species may have gotten out of it.
://www.sciencemag.org/news/2016/12/tibetan-dogs-can-survive-high-altitudes-thanks-ancient-breeding-wolves
http://www.theanimalfiles.com/mammals/carnivores/wolf_grey.html
http://science.sciencemag.org/content/333/6046/1084
New Noninvasive Alzheimer's Treatment
Recent studies conducted on mice, engineered to have Alzheimer's have revealed that light therapy greatly reduces the effects of the disease on the brain. Alzheimer's is an irreversible genetic condition that affects brain function (cognition and memory), and becomes worse over time. The brain becomes congested with beta-amyloid plaque, gamma oscillations become impaired, and begins to form abnormal tau proteins that form tangles in the brain.
Tests conducted at MIT treated diseased mice with light therapy, inducing gamma oscillations at 40 hertz for one hour, beta-amyloid levels dropped by 50%, the only drawback being that beta-amyloids fully recovered to previous levels within 24 hours of treatment. The light therapy also removes plaque and mutated tau proteins. This gamma oscillation also improves the brains overall ability to get rid of mutated or faulty proteins.
Overall I believe this finding is quite fascinating, and could possibly be a big breakthrough in science and the medical field. It is clearly stated that this study has only been done on mice, but everyone including myself has hopes the effect of light therapy will translate to human beings.
Tests conducted at MIT treated diseased mice with light therapy, inducing gamma oscillations at 40 hertz for one hour, beta-amyloid levels dropped by 50%, the only drawback being that beta-amyloids fully recovered to previous levels within 24 hours of treatment. The light therapy also removes plaque and mutated tau proteins. This gamma oscillation also improves the brains overall ability to get rid of mutated or faulty proteins.
Beta-amyloid plaques
Overall I believe this finding is quite fascinating, and could possibly be a big breakthrough in science and the medical field. It is clearly stated that this study has only been done on mice, but everyone including myself has hopes the effect of light therapy will translate to human beings.
Image taken from http://cdn1.medicalnewstoday.com/content/images/articles/314/314627/beta-amyloid-plaques-between-nerve-cells.jpg
Tuesday, December 13, 2016
MicroRNA: The Cure to Schizophrenia Voices?
Schizophrenia often occurs during late adolescence or early adulthood and is characterized by cognitive problems such as delusions and hallucinations. About 1.1 % of Americans are affected by schizophrenia every year. Despite schizophrenia being so common and having many treatments, there are still unanswered questions. One question in particular is the origin of auditory hallucinations.
Researchers at St. Jude Children's Research Hospital have been using mouse models in order to replicate genetic predisposition for schizophrenia. The model that researchers were studying in particular is the 22q11 deletion syndrome, also known as DiGeorge syndrome. By modeling this syndrome, it allows the researchers to observe the development of psychiatric conditions, some of which that lead up to the development of schizophrenia.
While running the mouse model, scientists have identified microRNAs that can be served as useful for creating new anti-psychotic drugs with reduced side effects. MircoRNAs are non-coding RNA molecules that generally involved in regulating and silencing gene expression. The specific microRNA that is of particular interest to researchers is miR-338-3p. This specific microRNA regulates the manufacture of protein D2 dopamine receptor (DRd2) in which have a major role in auditory hallucinations. According to Dr. Zakharenko, auditory hallucinations that are typical in schizophrenia is related to high levels of Drd2 in the auditory thalamus.
Through the mouse modeling, the researchers have discovered that individuals with 22q11 deletion syndrome are missing Dgcr8 genes in which is essential for the production of microRNAs. Because of the reduction of Dgcr8 genes based on this study, this leads to an increase in DrD2, thus causing auditory hallucinations demonstrated from schizophrenia. Further results have concluded that by replenishing microRNAs, the Drd2 levels decreased thus restoring normal functioning within the auditory thalamus, thus leading to a cure to auditory hallucinations. This is an important breakthrough for anti-psychotic drugs. By using a natural process and the concepts of microRNA, it can serve a new basis for how drugs for treating mental disorders are made. In particular, the benefits of microRNA is that it can lead to more effective interventions with limited side effects. With such an important discovery, this research can pave the way to tacking other mental disorders using the same concept. It will be very interesting to see how this research will progress and be beneficial in terms of psychiatric and medical research.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)





