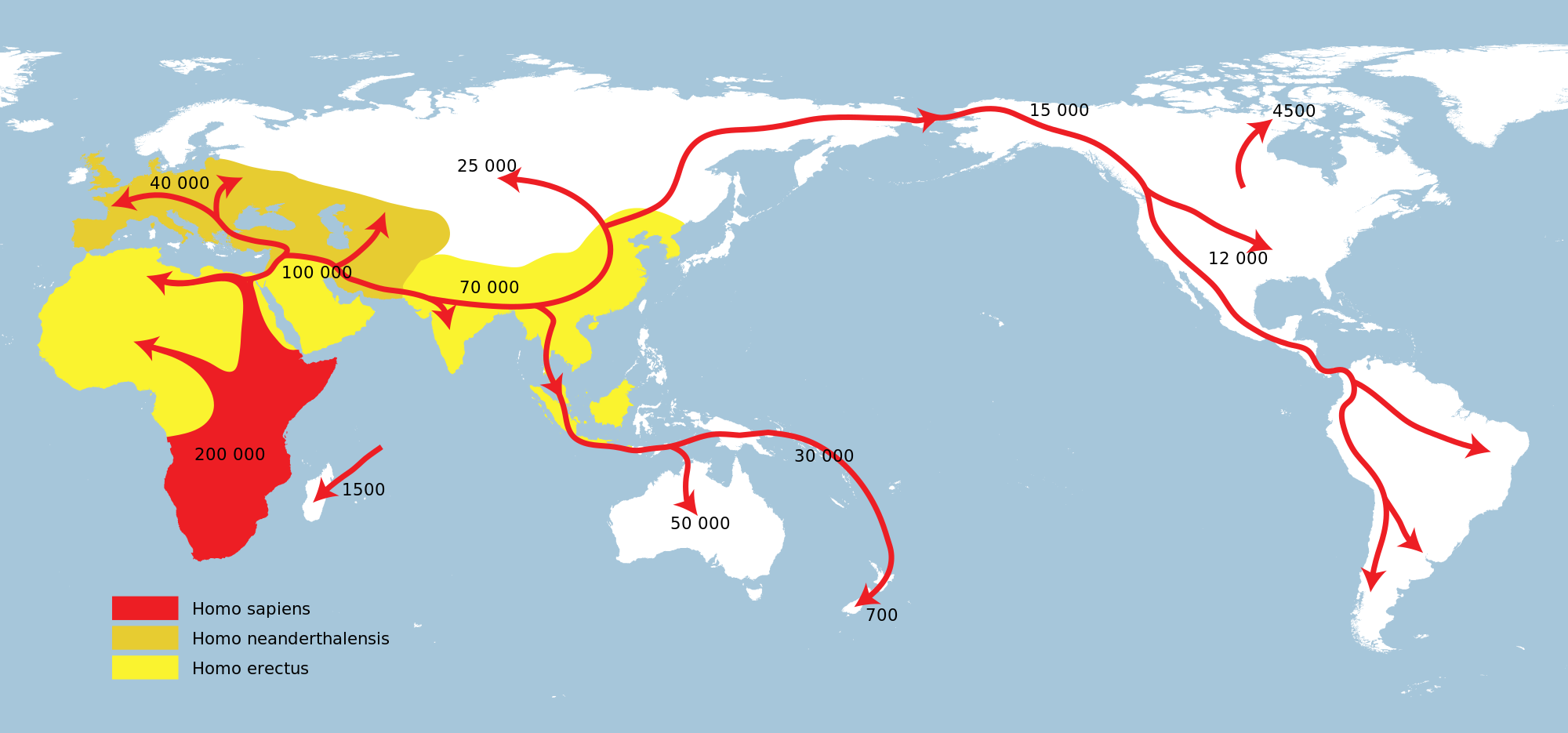
For the past decade, geneticists have been studying the link between migration patterns of human and genomic variation.
After analyzing the collected data, scientists were able to conclude an approximate time period that different populations migrated from Africa. For example, current studies show that about 2% of genomes from individuals of Papua New Guinean ancestry, their ancestors separated from Africa earlier than Eurasians did. Eurasian countries- land lying between Asia and Europe- include Russia, Belarus, Ukraine, Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan, Tajikistan, and Kyrgyzstan.
In addition to narrowing down the patterns of human migration, scientists have also discovered something else. Studying ancient DNA has shown that many large-scale populations have disappeared without a trace, except for their bones. This means that populations that used to live in Eurasia, for example, are no longer traceable by science.
To discover migration patterns and connections between different countries and genomic variation, has lead to many discoveries and many more questions. However, scientists are still researching more migration patterns, hoping to discover more secrets of our past.
More about human migration and genomic variation is provided below.
http://phys.org/news/2016-02-genome-human-migration-evolution.html
No comments:
Post a Comment