Evolutionary biologists sequenced seahorse DNA to understand their evolution, one like no other sea creature.
It has neither a pelvic fin nor tail, males give birth, they have no teeth, and bony plates reinforce its body; the seahorse is an evolutionary oddity and it is the prime subject for six evolutionary biologists that want to understand why. Their findings were astounding; they found that the loss and duplication of genes and the loss of regulative elements directly contributed to a rapid change in evolution.
Professo Axel Meyer identified, from genomic sequencing, that several genes that are present in fish teeth as well as human teeth development, are not found in seahorses. They evolved by the way they eat food, they suck up prey rather than bite and chew.
Curiously, they found that gene duplication influenced pregnancy in males. Duplicated genes can create an entirely new function, and this just so happens to be the pregnancy in males. The genes probably only regulates the process by which the babies leave the brood, but there still is much to learn.
The seahorse is an excellent organism to study because is shows how evolution can rapidly change and organism's appearance and function.
Wednesday, December 14, 2016
The evolution of Seahorses
Labels:
Evolution,
gene duplication,
genomic sequence,
seahorse
Adapting to Pollution, Quickly.
Pollution of our waterways is becoming a problem but one particular fish has been shown to have adapted to the excess level of pollution in the waters that they live in. Atlantic killfish that occupy polluted estuaries. The Atlantic killfish is a small slender fish that is native to the North American coast. (Banded killfish facts). The places they live have toxicity levels high enough to kill them and other larger fish. This is due to industrial plants that dump their waste into the estuary. Scientists from the University of California have examined these fished in order ti figure out how they are adapting so quickly. Their tests exhibited that the killfish is 8,000 times for resistant to these pollutants than other fish. The killfish is an important small food fish, meaning that it is the base food for most other bigger fish. It also is a bio-indicator, meaning that if the killfish suddenly start to take a dive them the surrounding ecosystem will be harshly affected.
The Atlantic killfish, like the one above, is special because it has very high levels of genetic variation, higher than any other vertebrate. The more genetic variation the faster evolution can act upon that creatures. The fish were taken from a multitude of different sites, including Massachusetts, New Jersey, Connecticut, and Virginia. Their test also concluded that their high levels of genetic variation were not due to the polluted enviorment, instead they were already present in the fish's genome. The Atlantic killfish has had the ability to adapt very quickly to changing enviorments. The study lay the frame for future research that can figure out which genes are used to deal with the chemical change. (University of California- Davis).
Banded killifish photos and facts. (n.d.). Retrieved December 14, 2016, from http://www.arkive.org/banded-killifish/fundulus-diaphanus/
University of California - Davis. (2016, December 8). Against the tide: A fish adapts quickly to lethal levels of pollution: What's its secret? And can humans learn from it?. ScienceDaily. Retrieved December 14, 2016 from www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2016/12/161208143334.htm
Labels:
Adaptation,
Evolution,
Genetic Variation,
Killfish,
pollution
Salt Tooth
Most people have heard of a sweet tooth but in recent discovery, there is also a gene relating to a "salt tooth"! During a study, the people with a variation of the gene, TAS2R48, were more likely to eat too much sodium or acquire a "salt tooth". There is a correlation between people with high blood pressure and their salt-intake. The study was presented as the American Heart Association's Scientific Sessions and many people found that identifying a gene like this is very helpful. If people know that they have the particular variation in the gene then they can be given individual guidance to help them prevent diseases like heart disease. People with the variation in the gene should eat about half the recommended amount of sodium (half of 2,300 mg).
When a gene like this is found it doesn't seem like it would be useful but then it was applied to a disease like heart disease it is very useful. I am curious to see the extent of the study and how far the identification of the gene helps other people. Maybe the discovery can lead to more identifications of genes!
Source: (other source in text)
http://www.livescience.com/56850-salt-taste-genetics.html
Labels:
#gene #variation,
#genetics,
#heartdisease,
#salt
Temperature Dependent Bacteria as a Remedy
A new study conducted at the Massachusetts Institute
of Technology shows that temperature dependent bacteria may be used in the
future. This treatment will be administered to patients by placing bacteria in
them. The bacteria will contain medicine that will be pumped into the body
based on the temperature of the bacteria. The bacteria will be changed in
temperature by use of ultrasound technology. Furthermore, if the individual has
a fever this will cause the bacteria to self-destruct and be expelled from the
body through defecation. This treatment may be useful in cancer patients
because bacteria tend to gravitate toward tumors. This is due to tumors
containing less oxygen.
This is
very interesting and informative. I hope to see more information on this topic in
the future. This will be very useful in medicinal technology. Doctors should look
more into this technology to treat their patients.
Labels:
Bacteria,
Biological Studies,
cancer,
cancer treatments,
Mice Studies,
MIT
Why Left Handedness?
Why is left handedness so puzzling? It only accounts for 12% of the world's population. Yet, so many famous people have been left handed as well as five out of our last seven presidents to Einstein to the first man on the moon. What is it, genetically speaking, about left handedness, that explains this phenomenon?
To begin, the left handed origins have been observed in Neanderthals. Scientists studied the grooves in their teeth from them scratches they made while carving their food up and found that one in every ten Neanderthal scratched their teeth towards the left side. This can give us some insight as to how long the genes have influenced left handedness. However, scientists still do not understand what genes and how many are in play to cause left handedness.
We do have a clue as to how it affects left handed people, however. Left handedness and intelligence seem to go hand in hand. Left handers disproportionately make up the small amount of people with a genius iq. For example, twenty percent of Mensa members (society where one must have a high iq) are left handed. For only about ten percent of left handed people making up the population, this is an interesting fact. There are some drawbacks to being left handed, however. 40% of schizophrenic people are left handed. Scientists believe this happens to left handed people who have equal access to both sides of the brain. This can cause complex messages to the brain that can result in misconnections in neural networks and thus causing the symptoms of schizophrenia. The science is not in on this yet, however.
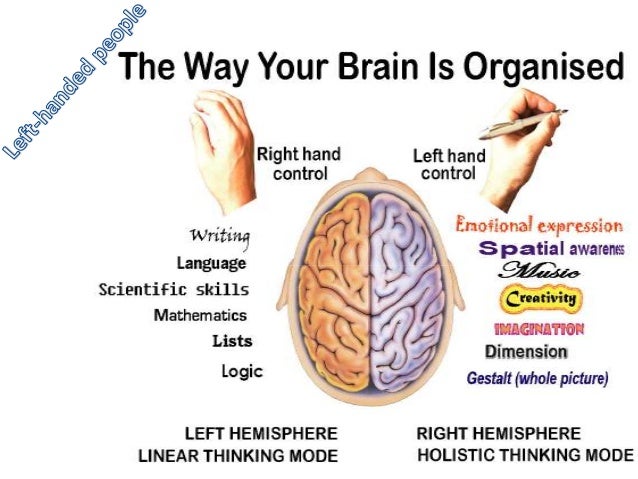
One thing is for sure. Left handedness should be studied more and understood. Many household names are left handed people that changed the world with their way of thinking. Science could have a breakthrough if they can understand how schizophrenia develops by studying the biological markers in left handed people. In any case, the left handed people are an important anomaly to understand, and essential in shaping our music, politics, and technology.
http://www.mirror.co.uk/news/technology-science/science/lefty-righty-here-astonishing-statistics-4757193
http://www.bbc.com/future/story/20160930-the-mystery-of-why-left-handers-are-so-much-rarer
http://www.anythinglefthanded.co.uk/being-lh/lh-info/advantages.html
http://healthland.time.com/2013/11/01/the-connection-between-left-handedness-and-schizophrenia/
To begin, the left handed origins have been observed in Neanderthals. Scientists studied the grooves in their teeth from them scratches they made while carving their food up and found that one in every ten Neanderthal scratched their teeth towards the left side. This can give us some insight as to how long the genes have influenced left handedness. However, scientists still do not understand what genes and how many are in play to cause left handedness.
We do have a clue as to how it affects left handed people, however. Left handedness and intelligence seem to go hand in hand. Left handers disproportionately make up the small amount of people with a genius iq. For example, twenty percent of Mensa members (society where one must have a high iq) are left handed. For only about ten percent of left handed people making up the population, this is an interesting fact. There are some drawbacks to being left handed, however. 40% of schizophrenic people are left handed. Scientists believe this happens to left handed people who have equal access to both sides of the brain. This can cause complex messages to the brain that can result in misconnections in neural networks and thus causing the symptoms of schizophrenia. The science is not in on this yet, however.

One thing is for sure. Left handedness should be studied more and understood. Many household names are left handed people that changed the world with their way of thinking. Science could have a breakthrough if they can understand how schizophrenia develops by studying the biological markers in left handed people. In any case, the left handed people are an important anomaly to understand, and essential in shaping our music, politics, and technology.
http://www.mirror.co.uk/news/technology-science/science/lefty-righty-here-astonishing-statistics-4757193
http://www.bbc.com/future/story/20160930-the-mystery-of-why-left-handers-are-so-much-rarer
http://www.anythinglefthanded.co.uk/being-lh/lh-info/advantages.html
http://healthland.time.com/2013/11/01/the-connection-between-left-handedness-and-schizophrenia/
Tibetan Dogs Able to Survive High Altitudes
A recent study shows that Tibetan dogs may have inherited their fitness at high-altitude, from breeding with Tibetan gray wolves around 24,000 years ago. This discovery somewhat mirrors the way that humans living at this altitude also inherited this type of fitness. Tibetans were found to have inherited this type of "high altitude gene" from and ancient, now extinct, species of human known as Denisovans, that another study found that humans interbred with around 40,000 years ago. This "high altitude gene" is a variant of a gene called EPAS1 that is found in the Tibetan mastiffs and regulates the production of hemoglobin. Scientists found that the most likely source of this variant of the gene in the Tibetan dogs, most likely came from the gray wolf.
Gray wolves also have a variant of the EPAS1 gene and found that the Tibetan gray wolf and Tibetan dogs most likely interbed 24,000 years ago, possibly from Tibetan dogs traveling with humans to higher altitudes. Another recent study showed that dogs may have only been domesticated around 16,000 years ago so this may show that the Tibetan mastiff may be one of the first and oldest dog breeds. The way this sort of mirrors how humans have been able to adapt to higher altitudes really shows how much different species have in common when it comes to the process of evolution, and makes you wonder why certain species interbred and what each species may have gotten out of it.
://www.sciencemag.org/news/2016/12/tibetan-dogs-can-survive-high-altitudes-thanks-ancient-breeding-wolves
http://www.theanimalfiles.com/mammals/carnivores/wolf_grey.html
http://science.sciencemag.org/content/333/6046/1084
Gray wolves also have a variant of the EPAS1 gene and found that the Tibetan gray wolf and Tibetan dogs most likely interbed 24,000 years ago, possibly from Tibetan dogs traveling with humans to higher altitudes. Another recent study showed that dogs may have only been domesticated around 16,000 years ago so this may show that the Tibetan mastiff may be one of the first and oldest dog breeds. The way this sort of mirrors how humans have been able to adapt to higher altitudes really shows how much different species have in common when it comes to the process of evolution, and makes you wonder why certain species interbred and what each species may have gotten out of it.
://www.sciencemag.org/news/2016/12/tibetan-dogs-can-survive-high-altitudes-thanks-ancient-breeding-wolves
http://www.theanimalfiles.com/mammals/carnivores/wolf_grey.html
http://science.sciencemag.org/content/333/6046/1084
New Noninvasive Alzheimer's Treatment
Recent studies conducted on mice, engineered to have Alzheimer's have revealed that light therapy greatly reduces the effects of the disease on the brain. Alzheimer's is an irreversible genetic condition that affects brain function (cognition and memory), and becomes worse over time. The brain becomes congested with beta-amyloid plaque, gamma oscillations become impaired, and begins to form abnormal tau proteins that form tangles in the brain.
Tests conducted at MIT treated diseased mice with light therapy, inducing gamma oscillations at 40 hertz for one hour, beta-amyloid levels dropped by 50%, the only drawback being that beta-amyloids fully recovered to previous levels within 24 hours of treatment. The light therapy also removes plaque and mutated tau proteins. This gamma oscillation also improves the brains overall ability to get rid of mutated or faulty proteins.
Overall I believe this finding is quite fascinating, and could possibly be a big breakthrough in science and the medical field. It is clearly stated that this study has only been done on mice, but everyone including myself has hopes the effect of light therapy will translate to human beings.
Tests conducted at MIT treated diseased mice with light therapy, inducing gamma oscillations at 40 hertz for one hour, beta-amyloid levels dropped by 50%, the only drawback being that beta-amyloids fully recovered to previous levels within 24 hours of treatment. The light therapy also removes plaque and mutated tau proteins. This gamma oscillation also improves the brains overall ability to get rid of mutated or faulty proteins.
Beta-amyloid plaques
Overall I believe this finding is quite fascinating, and could possibly be a big breakthrough in science and the medical field. It is clearly stated that this study has only been done on mice, but everyone including myself has hopes the effect of light therapy will translate to human beings.
Image taken from http://cdn1.medicalnewstoday.com/content/images/articles/314/314627/beta-amyloid-plaques-between-nerve-cells.jpg
Tuesday, December 13, 2016
MicroRNA: The Cure to Schizophrenia Voices?
Schizophrenia often occurs during late adolescence or early adulthood and is characterized by cognitive problems such as delusions and hallucinations. About 1.1 % of Americans are affected by schizophrenia every year. Despite schizophrenia being so common and having many treatments, there are still unanswered questions. One question in particular is the origin of auditory hallucinations.
Researchers at St. Jude Children's Research Hospital have been using mouse models in order to replicate genetic predisposition for schizophrenia. The model that researchers were studying in particular is the 22q11 deletion syndrome, also known as DiGeorge syndrome. By modeling this syndrome, it allows the researchers to observe the development of psychiatric conditions, some of which that lead up to the development of schizophrenia.
While running the mouse model, scientists have identified microRNAs that can be served as useful for creating new anti-psychotic drugs with reduced side effects. MircoRNAs are non-coding RNA molecules that generally involved in regulating and silencing gene expression. The specific microRNA that is of particular interest to researchers is miR-338-3p. This specific microRNA regulates the manufacture of protein D2 dopamine receptor (DRd2) in which have a major role in auditory hallucinations. According to Dr. Zakharenko, auditory hallucinations that are typical in schizophrenia is related to high levels of Drd2 in the auditory thalamus.
Through the mouse modeling, the researchers have discovered that individuals with 22q11 deletion syndrome are missing Dgcr8 genes in which is essential for the production of microRNAs. Because of the reduction of Dgcr8 genes based on this study, this leads to an increase in DrD2, thus causing auditory hallucinations demonstrated from schizophrenia. Further results have concluded that by replenishing microRNAs, the Drd2 levels decreased thus restoring normal functioning within the auditory thalamus, thus leading to a cure to auditory hallucinations. This is an important breakthrough for anti-psychotic drugs. By using a natural process and the concepts of microRNA, it can serve a new basis for how drugs for treating mental disorders are made. In particular, the benefits of microRNA is that it can lead to more effective interventions with limited side effects. With such an important discovery, this research can pave the way to tacking other mental disorders using the same concept. It will be very interesting to see how this research will progress and be beneficial in terms of psychiatric and medical research.
Rapid Evolution Saved This Fish From Pollution
The Atlantic killfish is a very common, minnow-like fish that lives in the rivers that boarder New Jersey and Pennsylvania. The fact that they lived there was very interesting to researchers because these waters are very toxic due to the toxic materials that run into them from surrounding factories. Chemicals like DDT and Agent Orange completely invade these waters, and in large volumes. They believe that it is an "evolutionary miracle" that they can survive these conditions because most organisms can not. Researchers did studies and found that these fish just have certain genetic adaptations no matter where they live; even if they do live in less polluted waters.
http://www.natureworldnews.com/articles/33874/20161212/killifish-mutant-fish-evolved-survive-toxic-polluted-waters.htm
Genetics of Cancer and How To Prevent It
Cancer is the underlining disease of the century. Why is this so? Statistics show that cancer is the second leading cause of death in America, totaling 564,800 people a year, or 1,500 deaths a day (TCLF, 2016). To understand how to prevent cancer, we first must understand what causes cancer. Cancer is essentially a process where old cells do not die and abnormal cells are created, which can form a tumor. These tumors grow and can spread throughout the body, making it incredibly hard to treat if it isn't caught early on (Cancer Center, 2016). The purpose of this blog is investigate some genetic situations where cancer tends to be prevalent.
One example of an inherited gene that primarily causes breast cancer in women and prostate cancer in men is the BRCA 1 gene. This level of inheritance is in 5-10% of people. The reason BRCA 1 can cause cancer is because of its function, or lack of functioning for a better term. BRCA 1 repairs DNA and can destroy malignant cells if DNA cannot be repaired. However, if the BRCA 1 gene is damaged, the possibility of cancer can rise up to 87% in women by the age of 70 because the gene can no longer repair DNA. This DNA becomes malignant since nothing is stopping it from mutating. DNA is a lot like a computer. If there is no anti-software (BRCA 1), viruses are much more likely in a computer and these viruses have the potential to destroy the inter-workings of the computer. In this case, cancer is rampant in women who have this gene.

A few other examples of genetic problems that lead to cancer is certain damaging habits. Smoking cigarettes in particular is a sure shot way of increasing the likelihood for cancer. An interesting find from British researchers revealed that a mutation occurs in our DNA per 15 cigarettes smoked. People that are smoking a pack of cigarettes a day are essentially mutating their DNA in that same day. As we discussed earlier, mutations in DNA is what cause cells to go haywire and multiply without any control. Other daily habits that can cause cancer include getting a root canal, eating synthetic foods (sweeteners), drinking fluoridated water, and even chronic stress!
It seems that there are so many ways to get cancer, so how can we protect ourselves? It's important to understand the genetic family tree and see how many people in the family are genetically predisposed to developing cancer. Also, be aware of the things you can control. For example, smoking is seriously harmful to health. Taking the extra steps to stop will potentially save years of life. Being proactive about what certain cancers keep popping up can go a long way in living a long, healthier lifestyle. Keep this in mind when you think about picking up that next cigarette or drinking that "synthetic" coffee.
http://www.dailymail.co.uk/health/article-1236597/Smoking-just-15-cigarettes-harms-DNA-finds-cancer-study-gene-mutation.html
http://www.thomlatimercares.org/Cancer_Facts.htm
http://www.naturalnews.com/041909_cancer_causes_daily_habits_healthy_living.html
http://www.cancercenter.com/what-is-cancer/
One example of an inherited gene that primarily causes breast cancer in women and prostate cancer in men is the BRCA 1 gene. This level of inheritance is in 5-10% of people. The reason BRCA 1 can cause cancer is because of its function, or lack of functioning for a better term. BRCA 1 repairs DNA and can destroy malignant cells if DNA cannot be repaired. However, if the BRCA 1 gene is damaged, the possibility of cancer can rise up to 87% in women by the age of 70 because the gene can no longer repair DNA. This DNA becomes malignant since nothing is stopping it from mutating. DNA is a lot like a computer. If there is no anti-software (BRCA 1), viruses are much more likely in a computer and these viruses have the potential to destroy the inter-workings of the computer. In this case, cancer is rampant in women who have this gene.

A few other examples of genetic problems that lead to cancer is certain damaging habits. Smoking cigarettes in particular is a sure shot way of increasing the likelihood for cancer. An interesting find from British researchers revealed that a mutation occurs in our DNA per 15 cigarettes smoked. People that are smoking a pack of cigarettes a day are essentially mutating their DNA in that same day. As we discussed earlier, mutations in DNA is what cause cells to go haywire and multiply without any control. Other daily habits that can cause cancer include getting a root canal, eating synthetic foods (sweeteners), drinking fluoridated water, and even chronic stress!
It seems that there are so many ways to get cancer, so how can we protect ourselves? It's important to understand the genetic family tree and see how many people in the family are genetically predisposed to developing cancer. Also, be aware of the things you can control. For example, smoking is seriously harmful to health. Taking the extra steps to stop will potentially save years of life. Being proactive about what certain cancers keep popping up can go a long way in living a long, healthier lifestyle. Keep this in mind when you think about picking up that next cigarette or drinking that "synthetic" coffee.
http://www.dailymail.co.uk/health/article-1236597/Smoking-just-15-cigarettes-harms-DNA-finds-cancer-study-gene-mutation.html
http://www.thomlatimercares.org/Cancer_Facts.htm
http://www.naturalnews.com/041909_cancer_causes_daily_habits_healthy_living.html
http://www.cancercenter.com/what-is-cancer/
Nailed It!
New DNA analysis of a fingernail supports the idea that lead poisoning was not the culprit of an explorer's death.
A 170-year-old mystery has been solved with a new, more detailed genetic map of a dead man's fingernail, John Hartnell. Lead poisoning was the leading cause of death (with good reason, it wasn't uncommon at the time; tainted water and food caused a lot of deaths) but now researchers have found evidence to prove that this was not the case.
Toxicologist Jennie Christensen and her colleagues measured levels of zinc and copper in different places of a fingernail and toenail of explorer Hartnell. They found that Hartnell was actually deficient for both metals (especially zinc) and could track the levels over his expeditions. The lack of zinc and copper was due to a lack of protein from meat and fish that is crucial to a person's diet. Hartnell's extreme zinc deficiency may have lead him to be susceptible to illness due to a weak immune response. Hartnell and his shipmates were vulnerable to pneumonia and tuberculosis and that is how they may have died.
A 170-year-old mystery has been solved with a new, more detailed genetic map of a dead man's fingernail, John Hartnell. Lead poisoning was the leading cause of death (with good reason, it wasn't uncommon at the time; tainted water and food caused a lot of deaths) but now researchers have found evidence to prove that this was not the case.
Toxicologist Jennie Christensen and her colleagues measured levels of zinc and copper in different places of a fingernail and toenail of explorer Hartnell. They found that Hartnell was actually deficient for both metals (especially zinc) and could track the levels over his expeditions. The lack of zinc and copper was due to a lack of protein from meat and fish that is crucial to a person's diet. Hartnell's extreme zinc deficiency may have lead him to be susceptible to illness due to a weak immune response. Hartnell and his shipmates were vulnerable to pneumonia and tuberculosis and that is how they may have died.
Using Vampire Bat Genetics to Predict Rabies Expansions in Peru
Rabies is a serious viral disease in animals that effects the central nervous system, ultimately leading to brain inflammation and death. This disease is most often transmitted through animal bites, scratches or salvia of infected animals. It causes serious public health risk in Latin America as it causes human death and the death of millions of dollars of livestock every year. The largest cause of rabies spread in Latin America is due to vampire bats and their blood-feeding diet. Although there are efforts to reduce vampire bat populations in epidemic areas, it has proved ineffective because the the death toll of humans and livestock is higher than before and the rabies virus is spreading to areas it was not before. Scientists have come up with the idea to use the genetic analysis of vampire bats in Peru to forecast the migration of the rabies disease. This research has led to the theory that the rabies virus will spread to the Pacific coast of Peru by the year 2020. Peru's Pacific coast is currently VBRV(Vampire Bat Rabies Virus)-free, however, evidence from testing the genomic sequences of vampire bats in VBRV-epidemic areas have given researchers insight on how the rabies virus is spreading and it suggests it is moving towards the coast. They analyzed 264 samples of rabies virus collected from livestock all over the country over fifteen years, and that it could be traced back to one of three common ancestors. The virus lineages were traced back the the east North Andes, east South Andes, and the inter-Andean valleys south of these areas. To collect data from the vampire bats, they used tissue samples from 468 vampire bats across Peru over five years and examined the mitochondrial DNA and the nuclear DNA. The data suggested that females did not move between different regions of Peru and that spatial distribution of the three location lineages was at fault of the male vampire bats. Based off of this information, scientists were able to create a map that forecasted future rabies invasions. To confirm their map's predictions, these scientists have been tracking livestock in their predicted areas and seen an increase in rabies spread toward the coast. Understanding how a disease spreads can allow us to prevent or control proliferation and prevent epidemics.
Rabies is most commonly associated with canines in the United States, or wildlife such as foxes, raccoons, and squirrels. However, in the United States the most common source of human rabies is from vampire bats as well. At every veterinary hospital, animal clinic, and wildlife rehabilitation clinic in the nation, it is required that every animal handled is up to date on it's rabies shot. Most jobs that require jobs handling wildlife, including my job with exotic birds and wildlife animal care center, require humans to receive a preliminary rabies vaccine before handling any animal that could possibly have rabies. It is the worst time anyone could have at the doctors to receive those shots. If an animal is suspected of having rabies, this is taken very seriously in the veterinary field. Since rabies is a disease that effects the central nervous system, and not blood or tissue or urine/feces, the way to test for an animal having rabies is extremely gruesome. The animal must be euthanized and the head must be decapitated and sent to a lab to test the brain tissue for rabies. This process may seem harsh, especially when it affects domesticated animals who bit someone and may not have rabies being euthanized and having their head removed to test, but it is the only accurate testing method for rabies. This is done so that the people who have come in contact with the rabid animal can receive medical treatment if the animal did in fact have rabies. This has happened at the practice I work for only a handful of times, and it never gets easier for anyone involved in the process. The spread of rabies in Peru being able to be tracked is one step closer in understanding the disease, and hopefully making strides toward it's containment.
Sources
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases, and Division of High-Consequence Pathogens and Pathology. "Learning about Bats and Rabies." Rabies. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 22 Apr. 2011. Web. 13 Dec. 2016. <https://www.cdc.gov/rabies/bats/education/>.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases, and Division of High-Consequence Pathogens and Pathology. "Rabies Basics." Rabies. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 05 Oct. 2016. Web. 13 Dec. 2016. <https://www.cdc.gov/rabies/>.
Escobar, Luis E., A. Townsend Peterson, Myriam Favi, Verónica Yung, and Gonzalo Medina-Vogel. "BAT-BORNE RABIES IN LATIN AMERICA." Revista Do Instituto De Medicina Tropical De São Paulo. Instituto De Medicina Tropical, Jan. 2015. Web. 13 Dec. 2016. <https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4325525/>.
National Geographic Society. "Desmodus Rotundus: Vampire Bat." Common Vampire Bat. National Geographic, 2016. Web. 13 Dec. 2016. <http://animals.nationalgeographic.com/animals/mammals/common-vampire-bat/>.
The New Jersey Department of Health, Communicable Disease Service, Infectious and Zoonotic Diseases Program, and Zoonotic Disease Unit. "Packaging and Transport of Animal Rabies Specimens to the New Jersey Rabies Laboratory." Rabies Laboratory Form. The New Jersey Department of Health, Mar. 2014. Web. 13 Dec. 2016. <https://www.nj.gov/health/cd/documents/faq/specimentophel.pdf>.
University of Georgia. "Scientists Use Genetic Analysis to Forecast Spatial Expansion of Rabies in Peru." Science News: Genetics. ScienceDaily, 16 Sept. 2016. Web. 13 Dec. 2016. <https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2016/09/160912161303.htm>.
Study in Cows Shows why Cloning Mammals Fails
Dolly was able to be cloned successfully because the technique of "somatic cell transfer" was used. However, cloning cattle is becoming difficult and the success remains low (fewer than 10% survive to birth). The main reason the cattle don't survive is embryonic death. Cloning cattle is important because it can be used to study mammalian development.
Harris Lewin, professor in the UC Davis Department of Evolution and Ecology, conducted a study using RNA sequencing to understand gene expression in cloned cows during implantation to discover why there is a high rate of failed pregnancy for cloned cows. The study combined the French's expertise in cloning and reproductive biology with the U.S.'s expertise in functional genomics. This collaboration lead to understanding the mechanisms that account for embryonic losses at implantation. The study also provided insight on how implantation events drive the progression of pregnancy and shape the phenotypes of the cattle after they are born.
The researchers studied the tissue of cloned cow embryos at 18 and 34 days of development and the endometrial lining of the cows pregnant with the clones. They also studied cows that conceived by artificial insemination with non-cloned cows. The study resulted in the finding of multiple genes that are expressed abnormally. This could explain why there is a high rate of death for cloned embryos. The researchers found abnormalities in the expression of more than 5,000 genes on day 18. Results also suggest that that the surviving clones were able to successful implant in the uterus and form a placenta, indicating that the losses of clones is due to problems of critical development genes in the extra embryonic tissue. The study also revealed other factors that could be leading to the death of the clones including problems with hormone signaling between the pregnant cow and the developing embryo.
I found this article to be fascinating. I thought if scientists were able to clone a sheep it would only be a short jump to cloning cows too. I didn't think that cloning cows in the same way as Dolly would be so difficult. This article makes me ask the question if any animals can be cloned the same way or if each animal has to be cloned separately. This study could possibly provide further insight to cloning other mammals.
Labels:
cattle,
cloning,
Dolly,
embryonic development,
gene expression,
RNA sequencing
The link between coeliac disease and wheat
When eating at a restaurant in America, one cannot ignore all the items that contain bread or pasta. Wheat is a crop that has become the soul of Americans; however, it can be toxic to people who suffer from coeliac disease. This is because wheat is a type of grain that contains gluten, which is a mixture of proteins that can be toxic to those individuals. When consumed, patients that have coeliac disease experience an immune response in their bodies to the gluten.
Coeliac disease is common in the US and affects people of all age groups both male and female. It is an autoimmune disease in which the lining of the small intestines becomes inflamed and flatted which leads to bowel damage.
Scientist are on the search for the elements that make gluten toxic. In an article published in the journal "Food Chemistry" scientists wanted to learn about the link between different wheats and their toxicity. They did this by analyzing various kinds of wheat from several countries; specifically epitopes which is a component in wheat that is responsible for the autoimmune response in patients. T-lymphocytes are a type of cell in the immune system that contain an antibody that is capable of recognizing the toxic component in wheat. The scientists look at how the T-cells responded to different wheats to determine its toxicity. Their results revealed that it is difficult to select for a variety of wheat with no toxicity because the genetic diversity is too great. The property of gluten is also related to the strength of the flour and the viscoelasticity of the bread dough. This study is a step towards revealing the potential of production practice for wheat safe for celiacs. It suggests the selective modification of toxic components.
Hopefully, this enables products to be developed that are safe for celiacs. It would improve the nutritional diets and quality of life for those people.
Coeliac disease is common in the US and affects people of all age groups both male and female. It is an autoimmune disease in which the lining of the small intestines becomes inflamed and flatted which leads to bowel damage.
Scientist are on the search for the elements that make gluten toxic. In an article published in the journal "Food Chemistry" scientists wanted to learn about the link between different wheats and their toxicity. They did this by analyzing various kinds of wheat from several countries; specifically epitopes which is a component in wheat that is responsible for the autoimmune response in patients. T-lymphocytes are a type of cell in the immune system that contain an antibody that is capable of recognizing the toxic component in wheat. The scientists look at how the T-cells responded to different wheats to determine its toxicity. Their results revealed that it is difficult to select for a variety of wheat with no toxicity because the genetic diversity is too great. The property of gluten is also related to the strength of the flour and the viscoelasticity of the bread dough. This study is a step towards revealing the potential of production practice for wheat safe for celiacs. It suggests the selective modification of toxic components.
Hopefully, this enables products to be developed that are safe for celiacs. It would improve the nutritional diets and quality of life for those people.
Promotion of Apoptosis in Cancer Cells
Healthy cells have an even balance of apoptosis
promoter proteins and anti-apoptosis promoter proteins. However, damaged cells
usually possess a higher ratio of apoptosis promoting proteins. This allows for
the destruction and degradation of cells that are not functioning properly. Unfortunately,
cancer cells do not work this way. The genetic alterations found in cancer
cells show an increased production in anti-apoptotic proteins. The result is a
damaged cell that is virtually invincible and will continue to divide and
produce more identical cells that are damaged. As stated in the article, there
are six known anti-apoptotic proteins. The main anti-apoptotic proteins found
in cancer are Bcl-1, Bcl-2, and Mcl-1. Currently, cancer treatments include,
chemotherapy, radiation, and immuno-therapy. These treatments promote the toxin
NOXA in cells, specifically cancer cells, and promote apoptosis of the cell. However,
the anti-apoptotic proteins oppose the effects of the toxin and allow the cell
to survive. This is observed in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia who
show resistance to chemotherapy.
Based
on the results of a study conducted at University of California Riverside scientists
should focus on the Bfl-1 protein. This protein is more abundant in humans
particularly. According to Maurizio Pellecchia, this protein is the main protein
in humans and not Mcl-1. Mcl-1 predominates in mice.
This article
is very interesting because if scientists can figure out a way to completely
inhibit the anti-apoptotic proteins in cancer cells it would be a great
treatment. The cancer cells would have no choice but to self-destruct. Furthermore,
the healthy cells would be unaffected by the cancer treatments. Other forms of
cancer treatment, such as chemotherapy and radiation, destroy healthy cells as
well as cancer cells. When cancer cells are targeted, the healthy cells will be
unchanged.
Labels:
apoptosis,
cancer,
cancer cells,
Cancer Treatment,
chemotherapy,
mice research,
protein,
radiation,
University of California
Asparagus!
Over the years, more and more research has been done to investigate why some people can smell the odor that asparagus gives their urine and others cannot. A new study found over 800 new reasons as to why this happens. Researchers studied the genes of roughly 7,000 people and found that there are ~870 genetic variants that are linked to the inability to smell the odor. When a group of random people were asked if they could smell the odor, 40% said yes, they could. Strange enough, more women than men said they could not smell the odor. Since the genes affecting this were already identified, they were able to tell which ones made it "possible" to smell the odor and which ones made it "not possible".
The study certainly has its limitations on how accurate it really is because you are asking a person (self-reported) if they can smell the odor. Once researchers find a new way to test this, other than by the person's self-reported answer, then it will be more accurate. However, I hope there is not much time spent on something like this considering all that can be discovered pertaining to genetics other than the genes that pertain to smelling the odor of asparagus of your urine. But maybe, something could come out of a it and it could lead to more discoveries.
Source: (other source is in text)
http://www.livescience.com/57199-why-some-people-cant-smell-asparagus-pee.html
Labels:
#asparagus,
#genes,
#genetic #variants,
#odor,
#self-reported,
#smell
Experimental Insecticide Explodes Mosquitos
In a new study by University of Vanderbilt shows a experimental molecule that causes kidney failure in mosquitos which leads them to explode.

https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2016/12/161206111712.htm
https://news.vanderbilt.edu/2016/12/01/investigators-explore-new-way-to-control-mosquitoes/
In a new study by University of Vanderbilt shows a experimental molecule that causes kidney failure in mosquitos which leads them to explode.
Vanderbilt pharmacologist Jerod Denton, Ph.D., Ohio State entomologist Peter Piermarini, Ph.D., and colleagues have aimed their study's at Anopheles gambiae which is the main cause of malaria in the world, and also Aedes aegypti which is the main transmitter of the Zika virus. Over decades mosquitoes evolve more and more to genetic resistance to insecticides which target their immune system. The study shows kidney failure, but not just kidney failure Malpighi an tubule failure.
"We're essentially preventing mosquitoes from producing urine after they take a blood meal," said Denton, associate professor of Anesthesiology and Pharmacology.
When a mosquito takes a blood meal their body weight at least doubles or triples in size. Besides providing nutrients to mosquitos blood meals also carry toxic salts which can depolarize cell membrane if not quickly voided. So this is all a rapid process to the mosquito. What the compound does would stop urine production the mosquito. After this happens the mosquito would swell up and burst. However this is only targeting the blood feeding mosquitos which are females.
"By targeting blood feeding female mosquitoes, we predict that there will be less selective pressure for the emergence of resistant mutations," Denton said
I believe this compound could greatly help in regulating mosquitos. It would also decrease the risk of malaria, Zika and other viruses.
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2016/12/161206111712.htm
https://news.vanderbilt.edu/2016/12/01/investigators-explore-new-way-to-control-mosquitoes/
Oxygen - The New Antibiotic
Along with being antibiotic resistant, bacteria have also adopted sleep as a form of survival. By using toxin antitoxin systems, bacteria can become dormant to resist antibiotic attacks and awaken as soon as their environment permits. These systems, also referred to as biofilm, are responsible for 80% of infections and are often the reason bacteria are referred to as antibiotic resistant.
The research also reveals that only 10% oxygen is enough to awaken the bacteria, and using the oxygen passageways, an entire colony of bacteria can be manipulated into breaking up and dispersing biofilm so an actual antibiotic may be able to attack the active bacteria.
Although interesting, I did not entirely understand how this information can be applied into a human bacterial infection. Normal blood oxygen levels can be anywhere from 95-100%, so how would this knowledge be applied when prescribing an antibiotic treatment? It probably is more useful as prophylactic, to prevent biofilms from forming in the body all together to prevent bacteria from going dormant in order to cure an infection faster.
Image taken from http://news.psu.edu/photo/441070/2016/12/08/toxin-antitoxin-002
Monday, December 12, 2016
How to Set Up Protozoan Mating Swarm, Bacteria Style
At the University of California, Berkeley, scientists were researching Salpinogoeca rosetta cells when they suddenly began to form mass mating swarms after exposure to an aphrodisiac produced by a bacteria. The bacteria in question that created the aphrodisiac was Vibrio fischeri. The bacterium creates chonodroitin sulfate (CS) lyase, in which is then released as a chemical signal that causes the cells to quickly aggregate and begin cell and nuclear fusion while duplicating and recombining their genetic material.
According to researchers, Nicole King and Ariel Woznica, this discovery has led to researchers to believe the possibility that environmental bacteria or bacterial symbionts can influence mating in animals as well. Part of the research at Berkeley was exploring the origins of multicelluarlarity. The research was mostly conducted on choanoflagellates such as the S. rosetta cells. Generally, researchers would monitor shared characteristics and behaviors that was common for evolution in animals. Based on the research, scientists have discovered symbiotic and pathogenic relationships between bacteria and multi-cellular animals. This relationship has been dated to even prehistoric times.
With this research, choanoflagelletes can serve as an excellent model organism in order to discover more information regarding the origins of multicelluarlity. By using these organisms, it can have an advantageous adaptation and uses in medicine. Supposedly, researchers can use choanoflagelletes as a means of mass drug production for cures by instilling the gene for the drug. By using bacteria to induce the cells to mass mating, it can cause a rapid supply of drugs based on a natural process within bacteria. This can certainly be very useful in the field of medicine.
Labels:
#bacteria,
cells,
Choanoflagellates,
envirnmental factors,
Mating,
symbiotic
Plants with Modified Fruit Fly Gene Used to Detoxify Contaminated Land
I think this could greatly improve the reduction of contaminated lands filled with TNT. Also this research could better help the way we edit genes in plants.
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2016/12/161207091315.htm
https://www.york.ac.uk/news-and-events/news/2016/research/contaminated-land-tnt-fruit-fly/
In recent research there has been a linkage in a gene expressed in common fruit fly's could be used to detoxify contaminated lands filled with TNT. Who knew the common fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster could hold the capabilities to enhance the effect of getting rid of TNT filled lands.
In the study published by New Phytologist it shows us how A gene in Drosophila melanogaster could be expressed in Arabidopsis a type of cabbage. This combination would improve the reduction of TNT in soil from past war eras. Scientists engineered the gene glutathione transferase to appear in the cabbage plant. The plant with this gene was evaluated and shown to be more resistant and were better able to remove TNT. The plant with this gene was compared to the wild type and was shown to better remove the TNT.
Professor Neil Bruce from the Centre for Novel Agricultural Products (CNAP) in the University of York's Department of Biology said "What is important about this transformation is that it converts TNT into a product that could be more amenable to being broken down in the environment.
I think this could greatly improve the reduction of contaminated lands filled with TNT. Also this research could better help the way we edit genes in plants.
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2016/12/161207091315.htm
https://www.york.ac.uk/news-and-events/news/2016/research/contaminated-land-tnt-fruit-fly/
Cancer Drugs May Threaten the Heart
Drugs that use the immune system to fight cancer have now been found to attack the heart in rare cases. Though only 1 percent of patients taking these medicines have developed these heart issues, each case has been severe and led to several deaths. In most cases, patients were taking two checkpoint inhibitors which caused their immune system to attack their heart. These drugs have been a breakthrough in cancer treatments and caused remission for many people, even those who were expected to die because they resisted previous treatments. Some hospitals have added cardiac testing for patients taking more than one checkpoint drug so they can find and stop this issue before it gets too severe. Dr. Benjamin A. Olenchock, a study author from the Division of Cardiovascular Medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston stated that, “As the number of patients treated with checkpoint inhibitors has markedly increased, rare cases of cardiac toxicity associated with the use of these cancer therapeutics, sometimes resulting in death, have been seen at multiple institutions including our own.” Doctors have suggested that using drugs to shut down inflammation in patients heart should stop the deterioration. But by stopping the inflammation by turning off the immune response it can also stop any of the benefits from the inhibitors. For now, there is no way to check a patients vulnerability to developing heart related issues from checkpoint inhibitors.
Labels:
cancer,
checkpoint,
heart,
immune system,
inhibitors
Atlantic Killifish Adaptation
Species change according to the surrounding environment for survival. This adaptation can take a couple of years or even millions demanding on the species. Most species become extincted before they are able to catch up to the environmental chances going on around them. For a species to go through evolution in a short period of times, that is able to adapt to the changing environment as it is happening around them means that the species could have a high rate of genetic diversity Most species though do not have such high genetic diversity.
A recent study was done on 400 Atlantic Killifish from a polluted/nonpolluted area. The study showed that they are "8,000 times more resistant" to pollution than any other fish studied (ScienceDaily). Scientist thought it could be genetic diversity but then discovered that the Atlantic Killifish already had a genetic variation for pollution, that allows them to adapt to such high polluted areas so quickly. While the other species are dying from the pollution or undergoing mutations (extra fin, 2 heads), the Atlantic Killifish comes out unharmed from all the pollution. There are not that many solutions to withstand pollution and this may be one of the limited adaptation to it.
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2016/12/161208143334.htm
Labels:
Adaptation,
Atlantic Killfish,
Evolution,
fish,
genetic,
Genetic diversity,
Genetic Variation,
pollution
Evolution of Killifish Allows Adaptation to Polluted Waters of New Jersey
The Passaic River and Newark Bay in New
Jersey are full of toxic pollutants, killing many fish and organisms in the
area. However, one of the most diverse vertebrates, the Atlantic killifish, has
managed to adapt to these conditions. Several independent populations of killifish have evolved different adaptations to the toxic environment.
Biologist Diane Nacci with the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and other
scientists compared 384 killifish genomes, finding that tolerance to this
pollution is found on the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) signaling pathway for
each of the populations, but that different nucleotide patterns were found in
each one. An environment that would kill killifish without the mutation can
house several different populations with slightly different mutations. Scientists
believe that the ability for killifish to adapt quickly are due to very large
populations, and therefore greater nucleotide diversity.
However, though some animal species have
the capacity to adapt to large amounts of pollution and effects from climate
change, that does not mean that all species are capable of that. It is likely
that only a select few species will have the capacity to mutate or evolve
resistance to human-induced effects such as pollution or accelerated climate
change. On a different note, if the water is cleared up again, the killifish
with the mutation for pollution resistance may not survive as well as killifish
without the mutation, though by that point most if not all of the killifish
without the pollution resistance in the area may have already gone extinct. It is
very important to look at the grand scheme of things, and if people continue to
contribute pollution and fossil fuels into the environment, species that are
low in numbers are unlikely to develop a resistance and are likely to go
extinct. Though this study gives clues into how natural selection operates
under extreme conditions, people should not let the planet and its living
creatures come to this point.
Labels:
Adaptation,
AHR pathway,
diversity,
Evolution,
killifish,
pollution
Talking Monkeys?
For years, researchers and scientists have been curious about primates and their ability to talk. We know that monkeys and chimpanzees are very smart, and have the ability to learn, but why don't they talk like us humans?
It is known that speech is one of the most powerful and a successful adaptation to humans. In order to understand why monkeys do not talk, researchers decided to do some experimenting. The first thing they looked at was the vocal tract of these animals, and realized that they are very similar to humans and have the ability to vocalize. But they believe that the monkey's brains are not wired properly to make speech and words. The adaptation of speech didn't only take place in our vocal tract, but also in our brains. As studies went on, the researchers discovered that monkeys can make a variety of different sounds, but also struggle with sounds, especially vowels.
http://www.sciencemag.org/news/2016/12/why-monkeys-can-t-talk-and-what-they-would-sound-if-they-could
It is known that speech is one of the most powerful and a successful adaptation to humans. In order to understand why monkeys do not talk, researchers decided to do some experimenting. The first thing they looked at was the vocal tract of these animals, and realized that they are very similar to humans and have the ability to vocalize. But they believe that the monkey's brains are not wired properly to make speech and words. The adaptation of speech didn't only take place in our vocal tract, but also in our brains. As studies went on, the researchers discovered that monkeys can make a variety of different sounds, but also struggle with sounds, especially vowels.
http://www.sciencemag.org/news/2016/12/why-monkeys-can-t-talk-and-what-they-would-sound-if-they-could
Early RNA may have used isolation strategy to defeat mutants
Tiny water droplets may have protected the first self-replicating molecules from parasitic mutants. Recent experimental evidence shows that temporary compartmentalization may help RNA molecules resist takeover by shorter, faster replicating mutants.
As the earliest self-replicating RNA strands reproduced, mutations would inevitably arise. Mutations which shortened the molecule, even at the expense of it's function, would have a selective advantage. Based on kinetic chemical principles, shorter and less complex mutants with the capacity to copy themselves more quickly and produce more offspring would push out longer, more advanced RNA molecules. This would cause evolutionary stagnation such that an RNA molecule would be limited in it's ability to grow increasingly more sophisticated. These mutants may therefore be considered parasitic in the sense that they have a high sexual fitness but have lost their genetic "instruction manual" to do anything else.
Mathematical models suggest that having RNA's replicate in many discrete populations instead of one giant gene pool would solve this problem. By simple probability, some pockets would end up with fewer parasites, and in these insulated compartments longer more complex RNA's might be able to get a foothold.
To test this idea in the lab, a German team retrieved a piece of RNA from a bacteriophage and pasted in a catalyst (ribozyme). They then let the RNA duplicate under different conditions with varying degrees of isolation to other RNA molecules -- either freely in a vial or distributed through a million microscopic water droplets in oil. The droplets held populations of RNA molecules together for short periods of time before breaking, letting the RNA mix together again, and then reforming with a different set of RNA inside. Catalytic activity of individual droplets was analyzed throughout the experiment.
Results concluded that after four generations of this repeating cycle, catalytic RNA that wasn't compartmentalized in any way had been completely overrun by parasitic RNA. However, compartmentalized RNA was shown to yield higher complexity, for somewhat surprising reasons. This being that complexity became advantageous due to competition between compartments, such that compartments with too many parasitic mutations died off compared to surrounding compartments with further advancing RNA. After 9 generations, a substantial amount of the functioning RNA still remained.
To quote Brian Paegel, a chemist at the Scripps Research Institute in Jupiter, Fla. "[cellularity] might have been totally central to life as we know it today." He states that it's becoming increasingly clear that compartmentalization helped to shape the emergence of life.
I found this study interesting, because it highlights a certain important biological reality that is often overlooked. This being that increasingly complex and more "advanced" (in the anthropocentric sense of the word) organisms are not the default direction of nature. Evolution will only take pathways which are absolutely necessary, and the most cost efficient, for propagation of a population under given environmental duress and condition. Was it not for the unique environmental conditions and isolation introduced via aerosolized droplets (or a similar container), organic complexity may very well have stagnated, and life itself may never have formed.
As the earliest self-replicating RNA strands reproduced, mutations would inevitably arise. Mutations which shortened the molecule, even at the expense of it's function, would have a selective advantage. Based on kinetic chemical principles, shorter and less complex mutants with the capacity to copy themselves more quickly and produce more offspring would push out longer, more advanced RNA molecules. This would cause evolutionary stagnation such that an RNA molecule would be limited in it's ability to grow increasingly more sophisticated. These mutants may therefore be considered parasitic in the sense that they have a high sexual fitness but have lost their genetic "instruction manual" to do anything else.
Mathematical models suggest that having RNA's replicate in many discrete populations instead of one giant gene pool would solve this problem. By simple probability, some pockets would end up with fewer parasites, and in these insulated compartments longer more complex RNA's might be able to get a foothold.
To test this idea in the lab, a German team retrieved a piece of RNA from a bacteriophage and pasted in a catalyst (ribozyme). They then let the RNA duplicate under different conditions with varying degrees of isolation to other RNA molecules -- either freely in a vial or distributed through a million microscopic water droplets in oil. The droplets held populations of RNA molecules together for short periods of time before breaking, letting the RNA mix together again, and then reforming with a different set of RNA inside. Catalytic activity of individual droplets was analyzed throughout the experiment.
Results concluded that after four generations of this repeating cycle, catalytic RNA that wasn't compartmentalized in any way had been completely overrun by parasitic RNA. However, compartmentalized RNA was shown to yield higher complexity, for somewhat surprising reasons. This being that complexity became advantageous due to competition between compartments, such that compartments with too many parasitic mutations died off compared to surrounding compartments with further advancing RNA. After 9 generations, a substantial amount of the functioning RNA still remained.
To quote Brian Paegel, a chemist at the Scripps Research Institute in Jupiter, Fla. "[cellularity] might have been totally central to life as we know it today." He states that it's becoming increasingly clear that compartmentalization helped to shape the emergence of life.
I found this study interesting, because it highlights a certain important biological reality that is often overlooked. This being that increasingly complex and more "advanced" (in the anthropocentric sense of the word) organisms are not the default direction of nature. Evolution will only take pathways which are absolutely necessary, and the most cost efficient, for propagation of a population under given environmental duress and condition. Was it not for the unique environmental conditions and isolation introduced via aerosolized droplets (or a similar container), organic complexity may very well have stagnated, and life itself may never have formed.
Labels:
compartmentalization,
Evolution,
mutation,
parisitism,
replication,
RNA
The Pepper Moth: Decoded

The black peppered moth, a famous example of adaptive evolution, recently had a major breakthrough in what exactly helped it change form pepper to black. Back in the 1800's, during England's industrial revolution, this moth adapted to its newfound, soot covered environment, by becoming darker, allowing it to blend in with the newly soot covered trees. This adaptation allowed for the darker moths to pass down their genes, and become the new wild type.
Recently it was discovered that this change was all due to a gene called "cortex", which in most organisms codes for the function of cell division. In moths, and butterflies, cortex was seen to code for wing and scale color. This is not the beginning of this abnormality. This gene is also known as a jumping gene, meaning that it can be found on different places all over the genome. Dr. Saccheri, an evolutionary ecologist, describes it as "[a] huge chunk of DNA that doesn't itself code for anything, but somehow disrupts the nature of a gene".
The fact that these moths and butterflies of the like use a gene that normally codes for cell division in order to code for something as simple as wing color. Also the fact that it is conveniently a jumping gene just adds to the strangeness of it's expression in the moth/butterfly.
http://www.nytimes.com/2016/06/02/science/moths-butterflies-dna-cortex-genes.html?rref=collection%2Fcolumn%2Ftrilobites
http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v534/n7605/full/nature17951.html
Labels:
butterflys,
cortex,
evolutionary adaptations,
Moths,
peppered moth
All About Von Willebrand Disease
Most people have heard of hemophilia, a blood disease causing people to injure easily and bleed more than normal. Von Willebrand Disease is a more common disease than hemophilia whose effects are the same. This disease affects about 1%of the U.S. population and is overlooked by people usually. One case was of a female who had this disease but was not aware. She always had heavy bleeding during her menstrual cycle but didn't think much of it until one day she was standing in a puddle of her own blood. She was then diagnosed with Von Willebrand disease. Many women such as her tend to overlook their heavy bleeding every month thinking it's normal.
Von Willebrand was a Finnish scientist who discovered this disease. The reason for the bleeding is due to the blood missing a key protein that causes it to clot. Although hemophilia and Von Willebrand disease both result in heavy bleeding due to an issue in blood clotting, their mechanisms are different. This results in heavy bleeding during the menstrual cycle of even from a small injury. There's 3 types of Von Willebrand disease, type 1 being the mildest and types 2 and 3 being genetic. In addition to easy bruising and bleeding, people might experience bleeding gums from simply brushing their teeth or bleeding of their gastrointestinal tract. Bleeding is usually seen from more than one place.
This disease can results in issues when it comes to pregnancy and child birth because of the possibility of the mother bleeding to death from giving birth. It's best to catch this disease early so infants can also be tested, especially since circumcision of little boys can also lead to heavy bleeding.
Treatment for this disease can be surgery or taking medication that contains the Von Willebrand factor that helps blood restore its ability to clot.
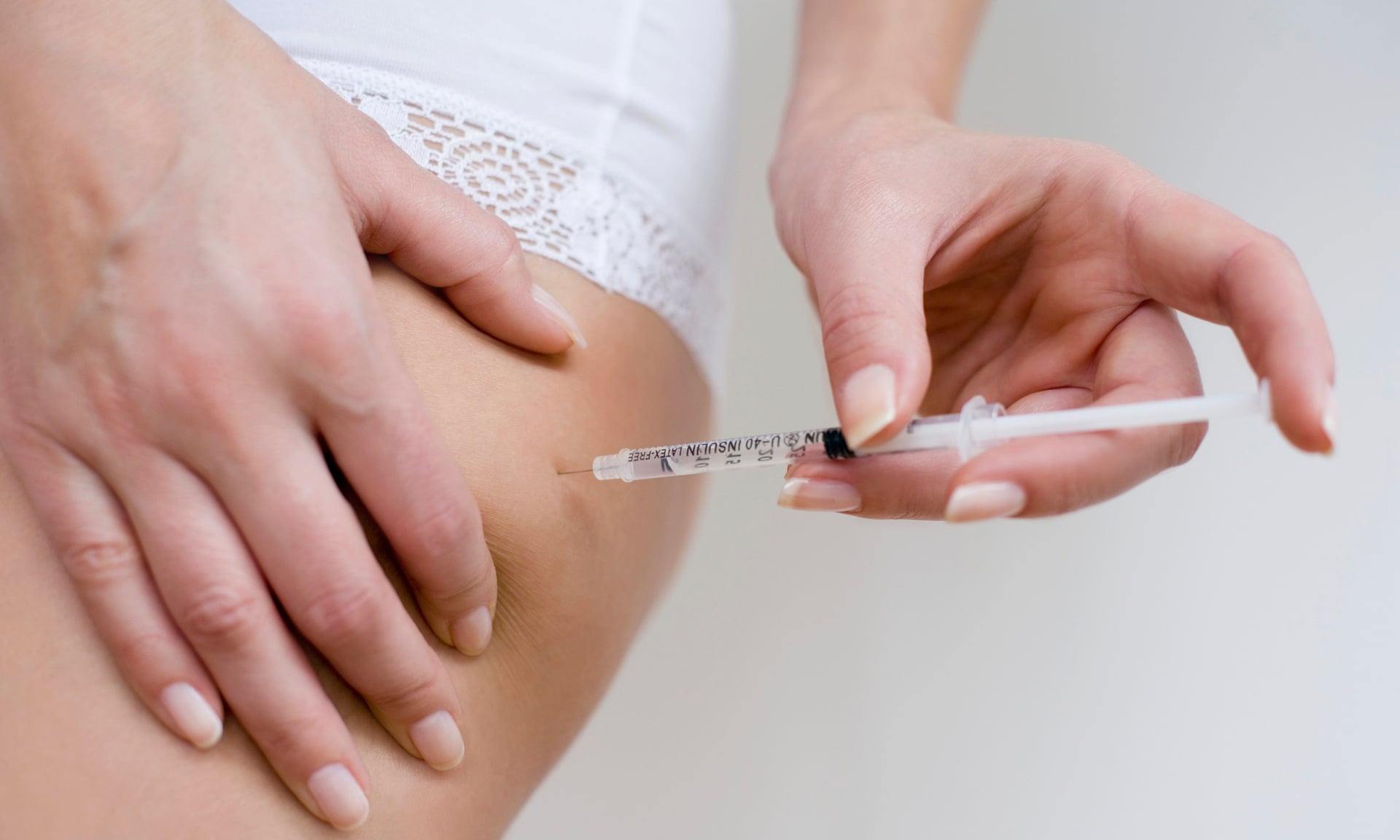
Insulin Injections are about to be a thing of the Past
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease that causes the
body to kill off all of its pancreatic beta cells. A new diabetes treatment can potentially eliminate the need to inject insulin, thanks to a cell-based treatment. Instead of insulin injections, a new diabetes treatment would include only having to get an implant. This implant would need to be replaced
only three times a year. In this new form of therapy, a capsule of genetically engineered cells would be implanted under the skin. This
capsule would release the needed amount of insulin just as an injection would.
In an experiment to test the safety, diabetic mice were
treated with these cells and ended up having normal blood sugar levels for
several weeks. Scientists are working hard to obtain a clinical trial license in order to test
this technology in patients. The treatment would be able to work with type 1and type 2 diabetes patients and scientists are hopeful to start testing in patients in little as 2 years. A lead
researcher at the ETH university in Basel, Martin Fussenegger, states, “By 2040,
every tenth human on the planet will suffer from some kind of diabetes”.
Fussenegger’s team re-engineered human kidney cells, or HEK cells to perform the
same function that the pancreas performs. It introduced two cells: one to make
them sensitive to glucose levels and another to instruct the cell to pump out
insulin when glucose levels exceeded a threshold. Overall, in the study, the
engineered HEK cells actually outperformed the normal pancreatic cells. The
ability of them to regulate blood sugar in mice worked very well. If this same
procedure can happen for humans, the cells would not need to be genetically
matched to the patient. The frozen capsules could be manufactured on an
industrial scale. This technique is said to be in the market within a decade.I think this would be an amazing advancement, considering that individuals would not need to inject insulin several times a day.
Labels:
beta cells,
blood sugar,
diabetes,
genetically engineered,
HEK cells,
insulin,
pancreas
E-Cigarettes in youth
In current times, electronic cigarettes (E-Cigarette) are very popular because it's smoking without smoking a cigarette. These E-Cigarettes turn nicotine into vapor which can be inhaled. It is proven to cause harm to brains of those who use them and just the air of the people around the users.
The study was performed on those who are off adolescent age, and not on adults. "Some researchers have said that e-cigarette use amount youth could act as a gateway to traditional smoking but the report says the relationship is not fully established."
http://www.nytimes.com/2016/12/08/health/e-cigarettes-united-states.html
Children's Hearing Loss
In modern times, children tend to block out the world with music: headphones being of help. The levels of music the children hear are different but are mainly high. When something is as loud as they have it at, they shouldn't be listening to it as much.
"Eighty decibels is twice as loud as 70 decibels and 90 is four times louder." No one should be listening to this type of level because " 100 decibels, about the volume of noise caused by a power lawn mower."
Parents tend to let their children use headphones for their children for multiple reason, watching. Movies, shows, or just listening to music. A study showed that "hearing loss in adolescents had increased to 19.5 percent in2005-2006 from 14.9 percent in 1988-1994.
http://www.nytimes.com/2016/12/06/health/headphones-hearing-loss-kids.html
Autism spectrum disorders: New genetic cause of identified
Autism
spectrum disorders (ASD) affect about one percent of the world's
population and are characterized by a range of difficulties in social
interaction and communication. A team of researchers led by Gaia Novarino,
Professor at IST Austria, has identified a new genetic cause of ASD. There
are many different genetic mutations causing autism, and
they are all very rare. A new
autism-linked gene was not only revealed, but it also identified the mechanism
by which its mutation causes autism. Mutations in other genes share the same
autism-causing method. They were able to identify mutations in a gene called
SLC7A5 in several patients born to consanguineous marriages and diagnosed with
syndromic autism. SLC7A5 transports a certain type of amino acids into the
brain. Researchers studied mice in which SLC7A5 is removed at the barrier
between the blood and the brain, to understand how mutations of SLC7A5 lead to
autism. They removed the gene from the mice and discovered that it caused an
interference with protein synthesis in neurons. The mice showed reduced social
interaction and behavioral changes. The researchers reintroduced the missing
SLC7A5 gene into the mice and after three weeks, improvements in behavior were seen.
Researchers found a potential treatment for a form of ASD only in mice. It is
going to take many more years of research until this process can be performed
on human patients. Before the study, autism spectrum disorders were always
thought to be irreversible conditions. The way they treated symptoms in the
mice cannot be directly used in humans. It showed that some of the neurological
complications presented by mice missing SLC7A5 can be rescued. So, it is
possible that patients may eventually be treated as well.
The fact that researchers found a potential
treatment for a form of ASD only in mice is still a great thing. That shows we are one step closer in finding a treatment for humans. Hopefully in a
few years, there will be results in potential treatments for autism spectrum
disorders for humans.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)